Steroid Treatment and Back Pain
Steroids (also known as corticosteroids) are drugs that reduce inflammation and decrease the activity of the immune system, so can help with the swelling, pain, tingling and numbness associated with some back problems. This can allow other treatments for back pain, such as physiotherapy and exercise, to start, and can also help people with back pain get back to normal daily activities.
Steroids are used short-term to treat back pain caused by inflammation, including herniated discs, degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, or sciatica (see our other articles for explanations of these conditions).
Steroids appear to work best if given soon after the beginning of the back pain.
Epidural Steroid Injections
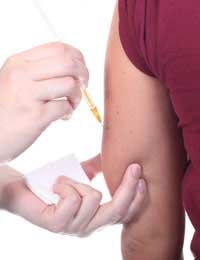
Epidural steroid injections – injections of steroids, often in combination with a local anaesthetic, into the epidural space, a space inside the bony spinal column – can be used to treat back pain.The anaesthetic, if included, immediately reduces the pain by numbing the nerves. The steroid reduces the inflammation, and should take effect within a few days to two weeks, with the effect lasting from a few weeks to a few months.
The epidural injection usually takes 10 to 20 minutes, and is often given after mild sedation. The epidural injection doesn’t need a stay in hospital. There may be some soreness, though the doctor will numb the skin before injection, and this discomfort should go in a couple of days. The epidural steroid injection can be repeated after two months if necessary, but treatment may be limited to three injections because of the risk of side effects.
Oral Steroids and Back Pain
Oral steroids can be used for back pain, and also reduce inflammation. Oral steroids are usually started with a high dose, which drops throughout the treatment, and are generally only used for one to two weeks because of the risk of side effects.Steroid Side Effects
Using steroids short-term should not cause many side effects – side effects are more common with high doses or long-term use, and not everyone will experience them.Using steroids long-term can increase the risk of weight gain, arteriosclerosis, cataracts and stomach ulcers, and can thin the skin, cause acne, lead to muscle weakness and affect wound healing. By affecting the absorption of calcium, steroids can lead to osteoporosis. Because steroids can reduce the activity of the immune system, they can make people more prone to infections. High doses can lead to bone necrosis, causing joint pain and damage, usually in the hip. Steroids can also affect mood and menstrual cycles. Use of steroids can increase blood sugar levels, so should not be used by diabetics. Talk to a doctor about any concerns over side effects.
Stopping Using Steroids
Because steroids taken for more than four weeks can reduce the body’s own production of natural steroids (cortisone), oral steroid treatment should be reduced (tapered) as the pain reduces, rather than stopped suddenly. This allows the adrenal gland to return to producing normal levels of cortisone.Business Energy With a Difference
If you are looking for business energy or need advanced solutions like remote energy monitoring, new supplies, downgrading or upgrading capacity, have a no obligation chat with Purely Energy.
To find our more get in touch here. or call 0161 521 3400.